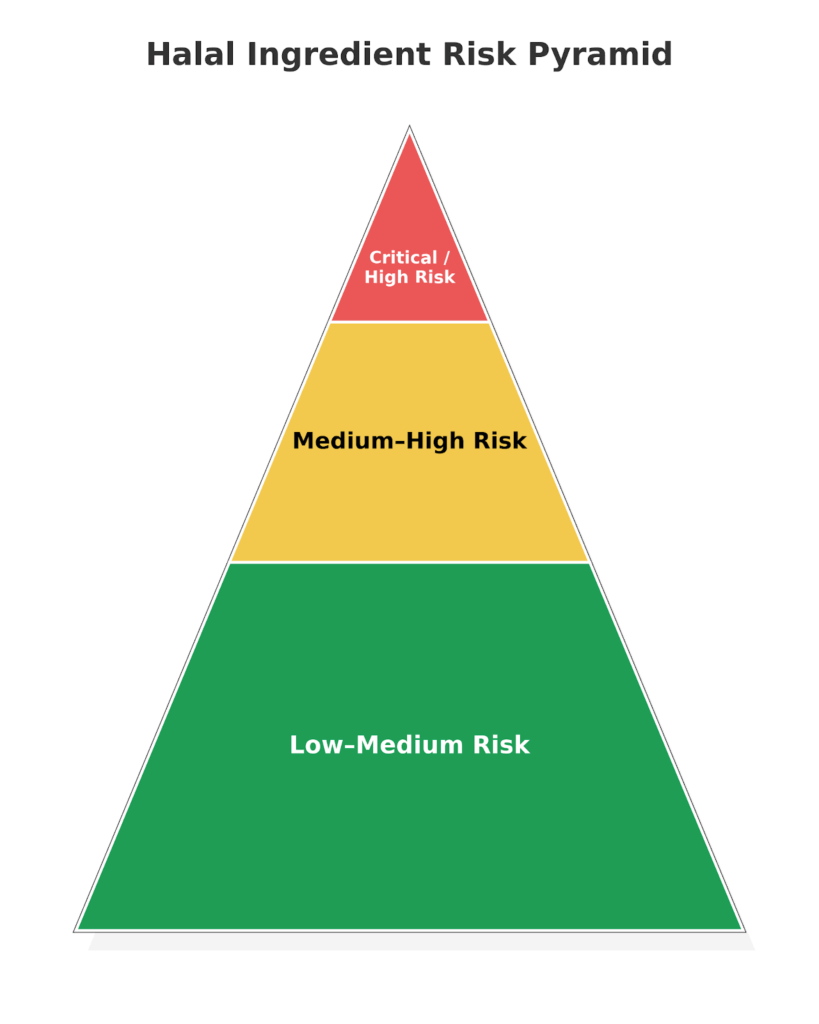
Ingredients and product categories can be ranked by their risk level in the Halal supply chain management, from low to critical.
This framework serves as a reference point for assessing ingredient halal risk levels. It’s important to note that risk categories, such as low, medium, or high are not absolute. An ingredient initially classified as medium risk may shift toward high risk depending on factors like its processing method, source of raw materials, and potential exposure to non-halal substances during production.
By defining the framework this way, the classification remains dynamic and context-dependent, helping auditors and manufacturers make informed halal integrity decisions across varied formulations and supply chains.
Disclaimer: This is a general guideline. Each raw material (RM) should be evaluated individually based on its source, processing method, and supplier documentation.
Here’s a ranking of Halal ingredients and products by risk level:
| General Classification of Halal Ingredients | |
| Classification | Examples |
| Low to Medium Risk Ingredients | Water (Non-hazardous)BeeswaxPure HoneyPure MilkLanolinFresh fishPlant and flower-based itemsFresh spices |
| Medium to High Risk Ingredients | Dairy products (cheeses, flavored UHT milks, flavored yoghurts, etc)Edible oilsVinegarVegan-certified productsDried Spices |
| Critical/High Risk Ingredients | Animal-derived ingredients: (meat/chicken/beef flavors, broths/stock/bouillon, lard, gelatin, glycerin, allantoin, yeast extract/autolyzed yeast, collagen/collagen peptides, marshmallows/gummies (gelatin-based), softgel capsules (gelatin), animal fats (lard, tallow, suet), shortening with animal fat, mono- and diglycerides (E471), oleic acid, palmitic acid, L-cysteine (feather/hair-derived), enzymes (animal rennet, lipase, enzyme-modified cheese, rennet casein/caseinates, rennet whey, cheeses made with animal rennet, shellac/confectioner’s glaze (E904)Insect derivatives: (e.g carmine) |
Halal Ingredient Classification By Sector
1) Food & Beverage
| Risk Level | Examples (representative, not exhaustive) |
| Low–Medium | Water; fresh fruits/vegetables; whole grains (wheat, rice, oats); legumes (soybeans, chickpeas, lentils); raw nuts/seeds; fresh fish; pure honey; beeswax (as glazing in primary production, not processed food); cane/beet sugar (raw/white); salt; botanical starches (corn/potato/tapioca); cocoa powder; tea/coffee beans; natural herbs; whole spices (unprocessed); baker’s yeast; vinegar mother (no added ethanol post); mineral salts (CaCl₂, KCl); plain fresh milk |
| Medium–High | Refined/“blended” edible oils; margarines/shortenings (veg); dried spices (cross-contact risk); flavorings (natural/artificial); colors (annatto, beta-carotene in carriers); vinegars (spirit, malt; processing solvent checks); caramel color (ammonia-sulfite process); malt extract/syrups; glucose/fructose syrups; dextrose; sugar alcohols (sorbitol, xylitol); citric/malic/lactic acid (fermentation media review); lecithin (unspecified source); mono/di-glycerides E471/E472 (unspecified); enzymes (microbial—media check); whey powder/caseinates (rennet status); smoke flavors; bread improvers; release agents/anti-caking (stearates) |
| Critical/High | Gelatin (all sources incl. bovine); collagen/peptides; animal fats (lard, tallow, suet); meat/chicken/beef flavors; broths/stock/bouillon; enzyme-modified cheese; animal rennet/lipase; rennet whey/caseinate; L-cysteine (feather/hair-derived); mono/di-glycerides from tallow; oleic/palmitic acid (animal); marshmallows/gummies (gelatin-based); confectioner’s glaze/shellac (E904); carmine/cochineal; blood plasma/binders; non-halal slaughtered meats; ethanol as an ingredient/solvent in final food; wine/rum flavorings in ethanol; shortening with animal fat |
2) Cosmetics & Personal Care
| Risk Level | Examples (representative, not exhaustive) |
| Low–Medium | Water; plant oils (argan, jojoba, olive, coconut); plant butters (shea, cocoa, mango); plant glycerin; aloe vera; hyaluronic acid (biotech); panthenol; niacinamide; vitamin C derivatives; mineral pigments (iron oxides); zinc/titanium dioxide; kaolin/clays; silica; candelilla/carnauba wax; beeswax (commonly acceptable in halal cosmetics); botanical extracts (solvent-free or verified) |
| Medium–High | Lanolin; squalane/squalene (unspecified source); stearic/palmitic/myristic acids (unspecified); cetyl/stearyl/cetearyl alcohol (origin unclear); PEG esters; polysorbates (20/60/80); glycerin (source unclear); tocopherol/vitamin E (carrier origin); emulsifying wax NF; surfactants (SLS/SLES with stearates); quats with fatty chains; fragrance (ethanol/denat alcohol); color lakes (binder checks); silicone emulsifiers with fatty anchors; opacifiers (stearates) |
| Critical/High | Gelatin (all types); collagen/elastin; keratin; carmine/cochineal; shellac; placenta/extracts; tallow-derived stearates; animal-derived glycerin; musk/ambergris; allantoin (animal-derived forms); bone char (rare in cosmetics but may appear in process aids); brush bristles from animal origin in product kits; animal-derived peptides; cholesterol (animal) |
3) Nutraceuticals & Supplements
| Risk Level | Examples (representative, not exhaustive) |
| Low–Medium | Minerals (Mg, Zn, Ca salts); synthetic/botanical vitamins (C, B-complex); HPMC/veg capsules; microcrystalline cellulose; rice flour; silicon dioxide; calcium carbonate; plant protein isolates (pea, rice); herbal extracts (water/verified solvents); MCT (coconut); inulin/FOS; citric/malic acid (verified media) |
| Medium–High | Gelatin capsules (source not declared); glycerin (capsule/plasticizer—source?); magnesium stearate/stearic acid (origin unclear); polysorbates; shellac enteric coatings (risk); flavors/colors (carriers); probiotics (bovine peptone/casein media?); enzymes (microbial—media check); omega-3 fish oil (softgel/gelatin issue); vitamin D3 (lanolin-derived—traceability); CoQ10 carriers; tinctures/extracts using ethanol; soft chew excipients (stearates, emulsifiers) |
| Critical/High | Softgels/gelatin (all); collagen peptides; chondroitin (bovine/porcine); glucosamine (shellfish—school dependent, plus processing aids); organ extracts; pancreatin/pepsin/trypsin (animal); carmine; shellac coatings; L-cysteine (feather/hair); rennet-derived caseinates; animal-sourced D3 or A with tallow carriers; bovine bile salts |
4) Packaging & Food-Contact Materials
| Risk Level | Examples (representative, not exhaustive) |
| Low–Medium | Glass; stainless steel; aluminum; virgin PET/HDPE/PP; silicone bakeware (food-grade); paperboard (uncoated); cork (untreated); inert liners (PTFE); simple fiber packaging (no coatings) |
| Medium–High | Recycled plastics (unknown additives); coated paper/boards; printing inks; adhesives (PVA with plasticizers—origin?); slip/antiblock agents (stearates); mold release agents; lubricants/greases (food-grade—origin check); wax coatings (blend origin); BOPP with fatty amide slip agents; primers/topcoats (fatty derivatives); reusable totes with conditioned lubricants |
| Critical/High | Casein-based adhesives; gelatin glues; tallow-based lubricants; shellac coatings; bioplastics containing casein/gelatin; fatty-acid-treated papers from animal origin; coating emulsions with animal glycerol; pallet/line lubricants with animal fats contacting packaging; compounded masterbatches using animal stearates in direct-food-contact layers |
5) Industrial Chemicals & Processing Aids
| Risk Level | Examples (representative, not exhaustive) |
| Low–Medium | Water; nitrogen/CO₂; inorganic acids/bases (HCl, NaOH); salts (NaCl, K₂CO₃); diatomaceous earth; activated carbon (plant); silica; calcium carbonate; propylene glycol; glycerin (plant-certified) |
| Medium–High | Ethanol (synthetic/fermentation; application-dependent); isopropanol (processing only, residuals check); enzymes (microbial—media check); polysorbates; PEGs; defoamers (source unclear); emulsifiers (stearates of Ca/Mg/Na—origin?); oleochemicals (fatty acids/alcohols, source unclear); fermentation nutrients (peptones/yeast extracts); antifoams (fatty derivatives); wetting agents with fatty chains |
| Critical/High | Animal-derived enzymes (pancreatic); tallow amines; oleic/stearic/palmitic acids from animal fat; calcium/magnesium stearates (tallow); peptones/caseinates (animal); fish-oil/tallow defoamers; blood-derived products; shellac resins in process coatings; animal-glycerin as solvent; animal-based release agents contacting food streams |
Supporting Documentation Required for Each Classification
| Classification | Examples | Documentation Required |
| Low to Medium Risk Ingredients | Soil & Water (non-hazardous), beeswax, pure honey, pure milk, lanolin, fresh fish, plant/flower-based items, fresh spices | • Basic Product Specification Sheet (PSS)• Ingredient Declaration (template will be provided by AHF)• Country of Origin Certificates (if applicable) |
| Medium to High Risk Ingredients | Dairy products (cheeses, flavored UHT milks, yoghurts), edible oils, vinegar, vegan-certified products, dried spices | • Halal Certificates or Suitability Statement from suppliers (if applicable)• Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)• Ingredient Declaration (template will be provided by AHF) |
| Critical / High Risk Ingredients | Animal-derived ingredients: meat/chicken/beef flavors, broths/stock/bouillon, lard, gelatin, glycerin, allantoin, yeast extract, collagen, marshmallows/gummies (gelatin-based), softgel capsules (gelatin), animal fats (lard, tallow, suet), shortening with animal fat, mono- & diglycerides (E471), oleic acid, palmitic acid, L-cysteine (feather/hair-derived), enzymes (rennet, lipase, etc.), rennet whey | • Valid Halal Certificates for each high-risk ingredient• Supplier Declarations of Compliance• Ingredient Declaration (template will be provided by AHF) |
Read More: A Comprehensive Guide to Halal and Haram Ingredients
Halal Certification and Contaminant/Allergen Control
Maintaining halal integrity from procurement till it reaches the end consumer requires careful attention on multiple fronts. With support from an authorized halal certification body, halal certification remains feasible when high-risk raw materials are present, provided scope and segregation are rigorously controlled.
The facility should inventory all high-risk materials and determine whether to eliminate/replace them, fully segregate them with dedicated rooms/lines, or exclude affected SKUs from the halal scope. Pork, non-halal certified animal proteins, and/or beverage alcohol must be confined to dedicated areas and equipment and may not share lines with halal production.
In cases where shared equipment is permitted, the facility shall validate cleaning and line clearance, schedule halal runs first or last (most certified manufacturers do this on Mondays or Fridays), use color-coded tools/PPE, and prohibit high-risk materials rework into halal batches. Moreover, compliance will also need to be demonstrated through supplier halal documentation, a concise HCCP/HAS plan, monitoring logs, and batch-release records.
Lastly, facilities with high-risk materials aiming for Halal certification must also ensure the shared lines and facility areas undergo a ritual and ATP verification backed sanitization procedure called Sertu.
Read More: What is Sertu? A Guide to Intensive Halal Cleaning and Using RLU
Get in Touch With AHF
Knowing the ingredients used in your product(s) helps with ensuring a streamlined route towards halal certification.
Get in touch with the American Halal Foundation to qualify your products for halal certification by sending us an email at info@halalfoundation.org or simply dialing in to us at +1 (630) 759-4981.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What does ingredient “risk level” or “sensitivity” mean in halal certification?
Ingredient sensitivity refers to the likelihood that a material could compromise halal integrity. Low-sensitivity ingredients usually require minimal verification, while moderate- and high-sensitivity ingredients (potential contaminants or allergens) need deeper scrutiny, documentation, and segregation.
Q. What documents are typically required for halal certification?
Documentation depends on ingredient sensitivity, but commonly includes:
- Product Specification Sheets (PSS)
- Supplier Halal Certificates
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
- Manufacturing Flowcharts & Cleaning SOPs
Q. Do vegan-certified products automatically qualify as halal?
No. While vegan products avoid animal derivatives, they may still contain:
- Non-halal alcohols or fermentation byproducts
- Cross-contamination risks from shared equipment
- A supplier halal certificate or review is still required for verification as some vegan products may contain ethanol..
Q. How does AHF verify halal compliance for suppliers?
AHF conducts supplier halal document reviews and, where needed, on-site audits. This ensures every ingredient and process step within the supply chain aligns with halal standards.
Q. How does this ingredient matrix help manufacturers?
The matrix guides manufacturers in:
- Reducing certification delays by addressing potential contaminants early
- Maintaining halal integrity across the entire supply chain
- Identifying ingredients that require additional scrutiny
- Preparing the right documentation upfront
Azmi Anees is a certification and compliance specialist working with the American Halal Foundation, where he focuses on global halal certification programs, integrated audits, and market-access strategy for food, cosmetic, nutraceutical, and ingredient manufacturers. He has worked closely with multinational brands and SMEs across North America, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. His insights emphasize on practical guidance for manufacturers looking to achieve halal compliance while improving operational efficiency and global market reach.